August marks two years of full compliance requirements under the GFSC Cyber Security Rules. The Rules closely follow NIST and NCSC guidance, neatly dividing an Information Security approach between its core elements of Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond and Recover. Whilst mandatory in the regulated sector, the GFSC recommends other businesses consider adoption of their Cyber Security Rules and Guidance. We believe that this is particularly apt for businesses in the financial service supply chain, such as law and accountancy.
Fines and advice were delivered by SEC (the US Financial Regulator) to eight firms who failed to implement adequate Cyber Security measures shortly after the GFSC Rules were published. Recently, the SEC proposed new rules, at their core requiring the adoption and implementation of effective Cyber Security policies and procedures – a good match for the GFSC Cyber Security Rules.
Organisations large or small, in the private or public sector, can benefit from reflecting on whether they meet the GFSC and NCSC advice. Clarity’s Cyber Security services range from full management and reporting to self-service with assistance where needed. With the right approach, matching the GFSC and NCSC guidance is within reach. Prerequisites for success include management support, a risk-based approach and knowledgeable staff. An open culture where human and technical failures are learned from and improvements are made without blame enables rapid whole organisation improvement.
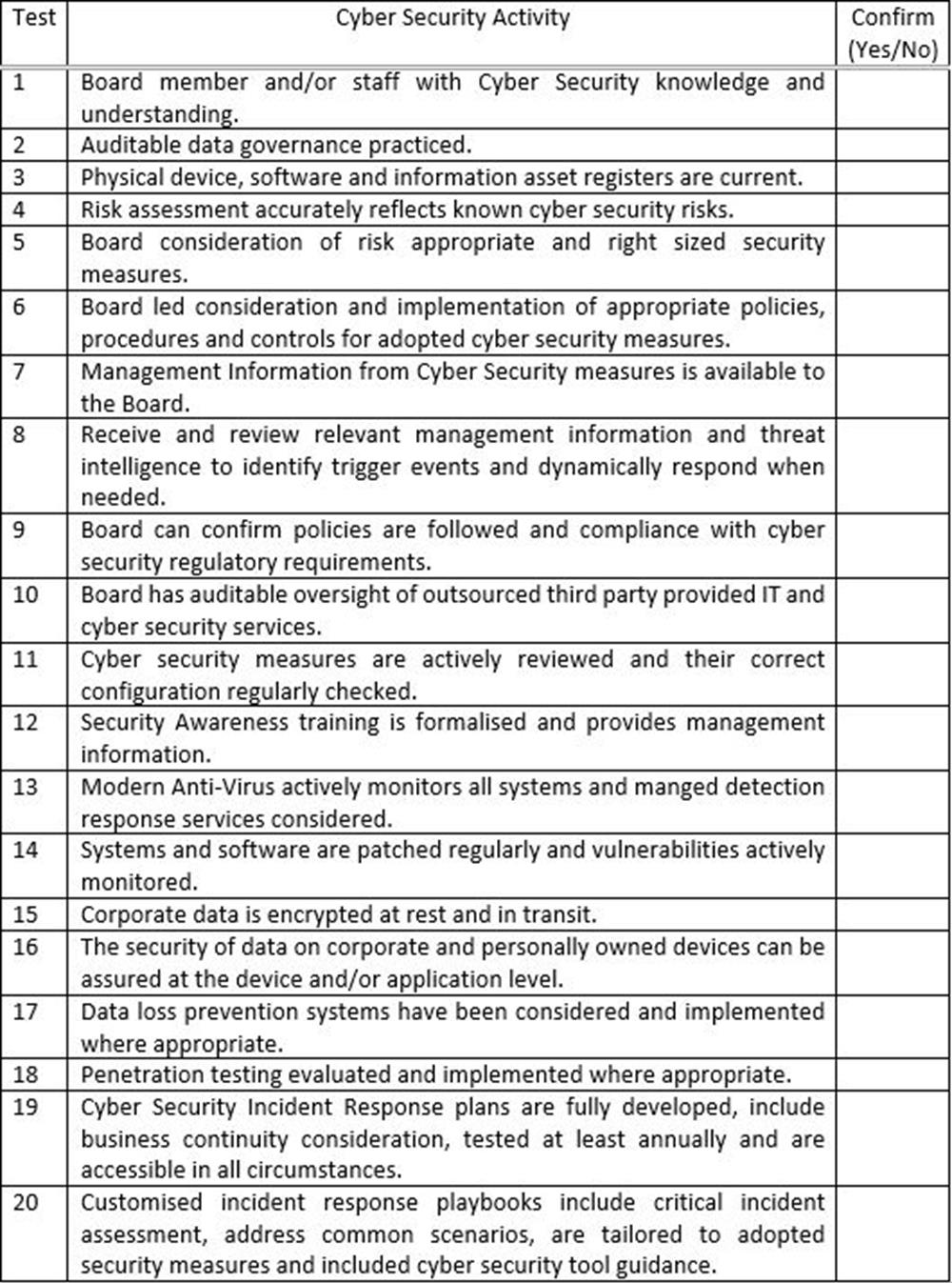
The remainder of this article summarises the key requirements to achieve better Cyber Security, with or without Clarity’s support. You can check out our Clarity News page if you’d like to read our in-depth reporting on meeting the GFSC Cyber Security Rules, recognised Cyber Security standards and review our non-technical, twenty-question compliance quiz.
Identifying Cyber Security needs starts with implementing right-sized and risk-assessed controls with matching Cyber Security policies and procedures. This approach aims to secure the overall confidentiality, integrity and availability of corporate data. Identifying Cyber Security risks, corporate systems, devices and information form an essential first step in delivering a cost and risk-appropriate approach.
Security Awareness training is a crucial component in the identification of threats and must match the dynamism of determined cyber attackers. The Rules reference a checklist of must have features, with an overarching requirement for systematic, continuous and updated training and a particular focus on new staff. Clarity delivers Security Awareness training in person by qualified and knowledgeable trainers, online via platforms we use ourselves and via themed in-office campaigns. The challenges are real and our approach is unapologetically enthusiastic, our priority is that our clients keep their first and best line of defence strong.
The regular discovery of system vulnerabilities via bespoke software identifies operating system, missing software, hardware patches and misconfiguration risks. Fake delivery, maintenance and consultancy staff are all popular approaches for testing the physical security of offices. A technique known as Penetration Testing has its Cyber equivalent via a point in time assessment, which identifies system vulnerabilities by real life attack simulations. Both techniques are valid, however, without staff security awareness training and remediation of identified physical and cyber vulnerabilities neither are cost-effective.
Protecting baselined systems against understood risks requires a regular review of existing security tools, products and services to ensure they are fit for purpose and correctly configured. Two examples are encryption and multi factor authentication. Checking that both function as intended to protect corporate data is essential. Securing corporate data on mobile devices is of equal importance to other company systems. Mobile Device Management software offers this capability at the device level, whereas Mobile Application Management secures data at the application level. Checking outbound communication for threats and unauthorised transfers is often overlooked. When correctly implemented, Data Loss Prevention measures can secure corporate data and reputations.
Detecting threats requires effective monitoring to capture and understand security events. Modern anti-virus software is a good example, offering advanced detection capabilities with warnings to match. Collating the notifications from anti-virus for all systems in a single dashboard provides data on current threats. When the approach is replicated across all detection systems, the holistic systems data which will deliver appropriate Management Information, that will inform Board security measure choices.
Responding to a Cyber Security event without the iterative improvement delivered by prior planning will lead to non-optimal outcomes. Simultaneous attacks can confuse and distract to allow a more serious compromise to occur. Clarity endorse GFSC guidance to use customised Incident Response Playbooks to co-ordinate Cyber Security incident response. Clarity provides company specific playbooks tailored to typical threat scenarios and incident response exercises. These exercises are engaging, well-planned and designed to fully test company security systems, management coordination, response under pressure and the ability to maintain business as usual.
Recovering from a Cyber Security incident is the penultimate step in incident response and may require the activation of unconnected secure backups. Having confidence that company backups will provide full disaster recovery capability if live systems are compromised and their data is no longer reliable or accessible is an important requirement. Once a system is recovered to a known good state, the lessons learned phase of an incident can inform risk assessment, Cyber Security measure and Board review.
Clarity’s Cyber team have many years of industry experience, which we use to effectively protect our clients’ systems and data. We provide pragmatic and easy to understand advice, practical support and effective protection for our clients.
The introduction to the Rules states its contents provide guidance and examples, which will not ‘be relevant to all firms’, although Boards are responsible for ensuring their ‘firm complies with the rules’. The table below poses twenty simple questions which seek to evaluate the majority of compliance issues and examples provided in the Rules. An inability to affirm any of the contentions made may still reflect compliance with the Rules for a Board which has made full consideration of their content and adopted a risk and right sized based approach. However, in the context of a widely connected supply chain Clarity believe all companies who can answer each question affirmatively will contribute to increased overall security in their business sector. If you’d like to discuss the results of the test confidentiality with our Information Security Department please do get in touch.